Materials:
Hofmann
apparatus with integrated platinum electrodes, stand, 30 Volt DC power
supply (alternative power supplies)
Left:
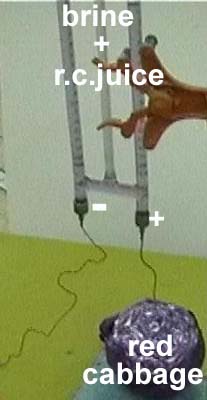
1. Boil extract a handfull of red cabbage juiceInsert steel electrodes
from paper clips into two rubber stoppers.
2. Close a
Hofmann Apparatus by these stoppers. 3. Fill the three tubes of the Hofmann
with a conc. solution of table salt in red cabbage juice.
4. Connect
its electrodes with a 30-Volt power source.
Observations:
Gas
bubbles at both electrodes (double volume at the negative electrode).Cathode
: The colour of the red cabbage juice changes from blue to green.
Anode:
The colour of the red cabbage juice changes from blue to red.
Explanation:Red:
4 H2O(l) + 4 e- --> 2 H2(g) + 4
OH-(aq)
Ox:
2
H 2O(l) --> O2(g) + 4 H+(aq) + 4
e -
Redox:
6 H 2O(l) --> 2 H2 (g) + O2
(g)
+ 4 OH-(aq) + 4 H+(aq)
Colour
change: The different
colours of the red cabbage juice result from acid base reactions of coloured
compounds called anthocyans (anthos = flower, kyanos = blue). Their cations
"are especially interesting because they behave much like the pH indicator..."
(S.S.Zumdahl, Chemistry) phenolphthalein.